Eating disorders are a serious issue in Australia, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the prevalence, risk factors, consequences, and treatment options for eating disorders in Australia, shedding light on the complexities of this condition and empowering individuals to seek help.
From anorexia nervosa to binge-eating disorder, we will explore the different types of eating disorders, their diagnostic criteria, and the impact they can have on physical, psychological, and social well-being. We will also discuss the role of media, social media, and cultural factors in promoting body dissatisfaction and contributing to the development of eating disorders.
Overview of Eating Disorders in Australia
Eating disorders are severe mental illnesses that affect a person’s relationship with food, body image, and weight. They are characterized by extreme and unhealthy eating behaviors that can lead to serious physical and psychological consequences. In Australia, eating disorders are estimated to affect around 1 million people, with young women being disproportionately affected.The
most common types of eating disorders in Australia are anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder. Anorexia nervosa is characterized by an intense fear of gaining weight, leading to severe food restriction and weight loss. Bulimia nervosa is characterized by episodes of binge eating, followed by purging behaviors such as vomiting, laxative abuse, or excessive exercise.
Binge-eating disorder is characterized by recurrent episodes of uncontrolled eating, often leading to feelings of shame and guilt.
Risk Factors for Eating Disorders
Eating disorders are complex mental health conditions that can have devastating consequences. While the exact causes are unknown, several risk factors have been identified that can increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing an eating disorder.
Risk factors for eating disorders can be broadly categorized into individual, social, and environmental factors. Individual risk factors include genetics, personality traits, and mental health conditions. Social risk factors include family dynamics, peer pressure, and cultural norms. Environmental risk factors include exposure to dieting and weight-loss messages, and the availability of unhealthy food options.
Role of Media and Social Media in Promoting Body Dissatisfaction
The media, including television, magazines, and social media, plays a significant role in shaping body ideals and promoting body dissatisfaction. The constant exposure to images of thin and idealized bodies can lead to negative body comparisons and a distorted perception of what is considered a healthy weight or appearance.
Social media, in particular, has become a breeding ground for body dissatisfaction and eating disorders. The use of filters and editing tools can create unrealistic body images, and the constant pressure to present a perfect online persona can lead to disordered eating behaviors.
Consequences of Eating Disorders
Eating disorders are serious mental illnesses that can have devastating consequences for both the physical and mental health of those who suffer from them. The consequences of eating disorders can be wide-ranging, and can include:
- Physical consequences: Eating disorders can lead to a number of physical health problems, including malnutrition, heart problems, kidney problems, bone loss, and gastrointestinal problems. In some cases, eating disorders can even be fatal.
- Psychological consequences: Eating disorders can also have a significant impact on mental health. People with eating disorders often experience depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. They may also have difficulty concentrating, making decisions, and controlling their emotions.
- Social consequences: Eating disorders can also have a negative impact on social relationships. People with eating disorders may withdraw from friends and family, and they may have difficulty functioning in social situations.
The long-term health risks associated with eating disorders are significant. People with eating disorders are at increased risk for developing chronic health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and osteoporosis. They are also at increased risk for dying prematurely.
Treatment Options
There are a number of different treatment options available for eating disorders. The best treatment option for a particular individual will depend on the severity of the disorder, the individual’s symptoms, and the individual’s preferences.
Treatment options for eating disorders include:
- Psychotherapy: Psychotherapy can help people with eating disorders to understand the underlying causes of their disorder and to develop healthier coping mechanisms.
- Medication: Medication can be used to treat the symptoms of eating disorders, such as depression and anxiety.
- Nutritional counseling: Nutritional counseling can help people with eating disorders to learn how to eat healthy and to maintain a healthy weight.
Treatment for eating disorders can be challenging, but it is possible to recover from an eating disorder. With the right treatment, people with eating disorders can learn to live healthy and fulfilling lives.
Seeking Help
If you or someone you know is struggling with an eating disorder, it is important to seek help. Eating disorders are serious mental illnesses, and they can be fatal if left untreated. There are many resources available to help people with eating disorders, and there is hope for recovery.
If you are concerned that you or someone you know may have an eating disorder, there are a number of things you can do:
- Talk to your doctor: Your doctor can screen you for an eating disorder and refer you to a specialist for treatment.
- Contact an eating disorder hotline: There are a number of eating disorder hotlines available that can provide you with information and support.
- Find a support group: Support groups can provide you with a safe and supportive environment to share your experiences and learn from others who are struggling with eating disorders.
Remember, you are not alone. There is help available, and you can recover from an eating disorder.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Eating Disorders
Eating disorders are serious mental illnesses that affect a person’s eating habits and body image. They can lead to severe health problems and even death. Diagnosis and treatment are essential for recovery.
The diagnostic criteria for eating disorders vary depending on the specific disorder. However, some common symptoms include:
- Extreme weight loss or gain
- Preoccupation with food or weight
- Distorted body image
- Binge eating or purging behaviors
There are a variety of treatment options available for eating disorders, including:
- Psychotherapy
- Medication
- Nutritional counseling
- Medical monitoring
The type of treatment that is best for a particular individual will depend on the severity of the disorder and the individual’s specific needs.
Early intervention and treatment are essential for recovery from an eating disorder. If you or someone you know is struggling with an eating disorder, please seek professional help.
There are a number of resources available for individuals and families affected by eating disorders, including:
- The National Eating Disorders Association (NEDA)
- The National Association of Anorexia Nervosa and Associated Disorders (ANAD)
- The Eating Disorders Coalition
Prevention and Early Intervention
Preventing eating disorders is crucial for the well-being of individuals and society. Strategies for prevention include promoting healthy body image, fostering positive self-esteem, and educating individuals about the risks of eating disorders. It’s essential to create a supportive environment that emphasizes acceptance and diversity, while challenging unrealistic beauty standards.Early
intervention is vital in addressing eating disorders effectively. If you suspect someone is struggling with an eating disorder, it’s important to approach them with empathy and concern. Encourage them to seek professional help from a qualified therapist or healthcare provider.
Early intervention can significantly improve the chances of recovery and prevent severe health complications.
Body Image and Self-Esteem
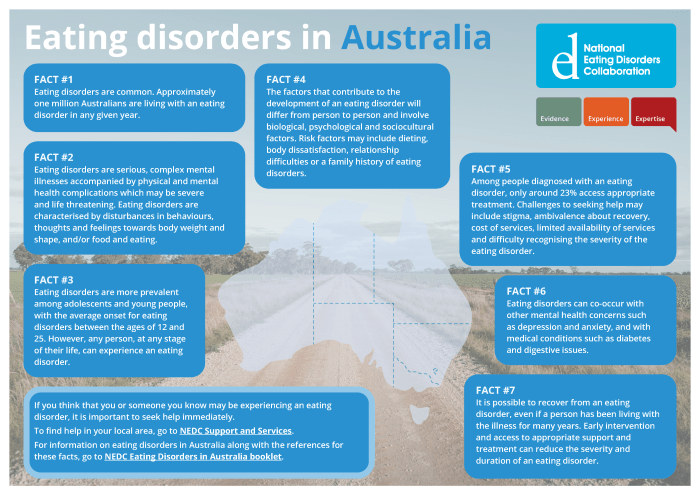
Body image refers to how an individual perceives and feels about their physical appearance. Self-esteem, on the other hand, encompasses a person’s overall sense of worth and value. Both body image and self-esteem play a significant role in the development and maintenance of eating disorders.Individuals
with negative body image often experience feelings of inadequacy, dissatisfaction, and shame regarding their appearance. This can lead to unhealthy behaviors, such as excessive dieting, body checking, and body avoidance. Negative body image can also contribute to low self-esteem, as an individual’s sense of self-worth becomes tied to their perceived physical attractiveness.Conversely,
positive body image and healthy self-esteem are important protective factors against eating disorders. When individuals have a positive body image, they are more likely to accept and appreciate their bodies, regardless of their size or shape. Healthy self-esteem allows individuals to feel valued and worthy, regardless of their external appearance.
Importance of Positive Body Image and Healthy Self-Esteem
Promoting positive body image and healthy self-esteem is crucial in preventing and treating eating disorders. This involves:
- Challenging unrealistic beauty standards and promoting diverse body representations
- Educating individuals about healthy eating and exercise habits
- Encouraging individuals to engage in activities that promote self-acceptance and self-care
- Providing support and resources for individuals struggling with body image issues and low self-esteem
By fostering positive body image and healthy self-esteem, we can create a more supportive and inclusive environment for individuals, reducing the risk of developing eating disorders.
Media and Eating Disorders
The media plays a significant role in shaping our perceptions of beauty and body image. Unfortunately, the portrayal of eating disorders in the media can have a negative impact on individuals, particularly those who are vulnerable to developing these disorders.The
media often portrays eating disorders as glamorous or desirable, which can lead to a distorted view of these serious mental illnesses. Individuals may come to believe that eating disorders are a way to achieve the “perfect” body, which can lead to unhealthy eating behaviors and body dissatisfaction.
Impact of Media Images on Body Image and Eating Behaviors
Research has shown that exposure to media images of thin and idealized bodies can lead to body dissatisfaction and negative body image. This can be particularly harmful for individuals who are already struggling with low self-esteem or a history of eating disorders.Exposure
to media images of eating disorders can also normalize these behaviors and make them seem more acceptable. This can lead to individuals engaging in disordered eating behaviors, such as skipping meals, purging, or excessive exercise, in an attempt to achieve the same body type as the models or celebrities they see in the media.
– Analyze the specific features of social media platforms that contribute to the promotion of eating disorders (e.g., idealized body images, pro-eating disorder content, social comparison)
Social media platforms offer an array of features that can contribute to the promotion of eating disorders, exacerbating body image concerns and disordered eating behaviors.
Idealized Body Images : Social media platforms showcase a plethora of images portraying idealized body types, often unrealistic and unattainable. This constant exposure to unrealistic beauty standards can lead to body dissatisfaction, fueling negative self-perceptions and disordered eating patterns.
Pro-Eating Disorder Content
Certain social media platforms harbor pro-eating disorder content, explicitly promoting and encouraging disordered eating behaviors. This content glorifies eating disorders, providing tips and tricks for weight loss and perpetuating harmful myths about body size and shape.
Social Comparison
Social media platforms foster a culture of comparison, where individuals constantly compare their appearance and bodies to others. This relentless comparison can exacerbate body dissatisfaction, leading to negative self-evaluations and increased risk of eating disorders.
– Explore the influence of culture on eating behaviors and body image
Culture exerts a profound influence on eating behaviors and body image, shaping individuals’ perceptions of what constitutes an ideal body and influencing their eating habits. Cultural factors, such as traditional values, social norms, and media representations, can contribute to the development and maintenance of eating disorders.
Individuals from diverse cultural backgrounds may face unique challenges related to eating disorders. For instance, in cultures that emphasize thinness and equate it with beauty and success, individuals may feel pressure to conform to these ideals, leading to disordered eating behaviors.
Conversely, in cultures that value larger body sizes, individuals may experience stigma and discrimination if they do not meet these expectations.
Cultural Factors Contributing to Eating Disorders
- Idealized body images: Cultural norms and media representations often portray unrealistic and unattainable body ideals, which can lead to body dissatisfaction and disordered eating behaviors.
- Social comparison: Social media platforms and other forms of media encourage individuals to compare themselves to others, which can foster feelings of inadequacy and negative body image.
- Cultural beliefs about food and weight: Certain cultures may have specific beliefs about the healthiness or desirability of certain foods, which can influence eating habits and contribute to disordered eating.
- Family and community influences: Family members and community members can play a significant role in shaping eating behaviors and body image, both positively and negatively.
Cultural Factors Shaping Body Image and Self-Esteem
- Cultural norms and values: Cultural norms and values can influence individuals’ perceptions of their own bodies and their self-worth.
- Media representations: Media representations of different body types can shape individuals’ expectations and perceptions of what is considered attractive or desirable.
- Family and community influences: Family members and community members can provide support and encouragement for positive body image, or they can contribute to negative body image through criticism or unrealistic expectations.
Statistics and Trends
Eating disorders are a serious public health concern in Australia, affecting individuals of all ages, genders, and socioeconomic backgrounds.
The prevalence of eating disorders in Australia is estimated to be around 1% of the population, with anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa being the most common types. Eating disorders are more common in females than males, with females being 10 times more likely to develop an eating disorder than males.
Age
Eating disorders can develop at any age, but they are most commonly diagnosed in adolescence and young adulthood. The average age of onset for anorexia nervosa is 16 years, while the average age of onset for bulimia nervosa is 18 years.
Gender
As mentioned earlier, eating disorders are more common in females than males. This is likely due to a combination of biological, psychological, and social factors.
Socioeconomic Status
Eating disorders are more common in individuals from higher socioeconomic backgrounds. This is likely due to a combination of factors, including increased exposure to media images that promote thinness, and greater access to resources that can facilitate eating disorder behaviors (e.g.,
diet pills, laxatives).
Trends
The prevalence of eating disorders in Australia has been increasing over the past few decades. This is likely due to a combination of factors, including changes in diagnostic criteria, increased awareness of eating disorders, and changes in social and cultural norms.
Impact of Social Media and Other Cultural Factors
Social media and other cultural factors can play a significant role in the development and maintenance of eating disorders. Social media platforms often promote idealized body images, which can lead to body dissatisfaction and disordered eating behaviors. Additionally, social media can provide a platform for individuals with eating disorders to connect with others who share their experiences, which can reinforce their disordered thoughts and behaviors.
Government and Policy
Governments have a crucial role in addressing the issue of eating disorders. They can implement policies and initiatives to promote awareness, improve prevention, and enhance access to treatment.
One key area of government involvement is the development of national guidelines and policies for eating disorders. These guidelines provide guidance to healthcare professionals, educators, and the general public on the identification, assessment, and treatment of eating disorders. They also Artikel strategies for prevention and early intervention.
Funding for Research and Treatment
Governments can provide funding for research into eating disorders. This research can help to improve our understanding of the causes and risk factors for eating disorders, as well as develop more effective treatments.
Governments can also provide funding for treatment services for people with eating disorders. This funding can help to ensure that people have access to the care they need, regardless of their financial situation.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Governments can conduct public awareness campaigns to educate the public about eating disorders. These campaigns can help to reduce stigma and discrimination associated with eating disorders, and encourage people to seek help if they are struggling with an eating disorder.
School-Based Programs
Governments can implement school-based programs to promote healthy eating and body image. These programs can help to prevent eating disorders by teaching young people about the importance of a healthy diet and exercise, and by challenging unrealistic body ideals.
Collaboration with Non-Profit Organizations
Governments can collaborate with non-profit organizations that provide support and services to people with eating disorders. These organizations can provide a range of services, including support groups, counseling, and advocacy.
– Review recent research on eating disorders, including studies on epidemiology, etiology, and treatment outcomes
Recent research on eating disorders has provided valuable insights into their epidemiology, etiology, and treatment outcomes. Epidemiological studies have shown that eating disorders are prevalent across different populations, with anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa being the most common types. Research on etiology has identified both genetic and environmental factors as contributing to the development of eating disorders, with a complex interplay between biological, psychological, and sociocultural influences.
Treatment outcome studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of various interventions, including psychotherapy, medication, and nutritional counseling, with a focus on individualized and evidence-based approaches.
Genetic Factors
Twin and family studies have shown that genetic factors play a role in the development of eating disorders, with heritability estimates ranging from 20% to 50%. Specific genes have been identified that may be associated with an increased risk of developing an eating disorder, such as genes involved in serotonin and dopamine neurotransmission.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors also contribute to the development of eating disorders. These include cultural factors, such as the emphasis on thinness in Western society, as well as family factors, such as parental criticism or pressure to achieve. Other environmental factors that have been linked to eating disorders include childhood trauma, bullying, and peer pressure.
Treatment Outcomes
Treatment for eating disorders typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and nutritional counseling. Psychotherapy approaches that have been shown to be effective include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), family-based therapy (FBT), and interpersonal therapy (IPT). Medication, such as antidepressants and antipsychotics, may also be used to manage symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive thoughts.
Nutritional counseling is essential to help individuals with eating disorders develop healthy eating habits and restore their physical health.
Personal Stories and Experiences
Eating disorders are complex mental illnesses that can have devastating consequences for individuals and their families. Personal stories and experiences can provide valuable insights into the challenges and triumphs of recovery.
Individuals with eating disorders may experience a range of symptoms, including distorted body image, disordered eating behaviors, and emotional distress. The journey to recovery can be long and difficult, but it is possible with the right support.
Challenges of Recovery
- Overcoming negative body image and self-esteem issues
- Learning to eat healthily and develop a positive relationship with food
- Managing emotional triggers and coping with stress
- Building a strong support system
- Challenging societal pressures and unrealistic beauty standards
Triumphs of Recovery
- Developing a healthy body image and positive self-esteem
- Enjoying a healthy and fulfilling relationship with food
- Learning to cope with stress and emotional triggers in a healthy way
- Building a strong and supportive community
- Living a full and meaningful life
Resources and Support
Individuals with eating disorders can access a range of support services to help them recover and manage their condition. These services include support groups, helplines, and online resources.
Support groups provide a safe and supportive environment where individuals can connect with others who understand their experiences. Helplines offer confidential support and information to individuals and their families. Online resources provide information on eating disorders, treatment options, and support services.
Support Groups
| Resource Name | Contact Information | Description |
|---|---|---|
| National Eating Disorders Association (NEDA) | 1-800-931-2237 | NEDA provides support groups for individuals with eating disorders and their families. |
| The Eating Disorders Coalition (EDC) | 1-888-375-7767 | The EDC provides support groups for individuals with eating disorders and their families. |
| Eating Recovery Center (ERC) | 1-877-931-2237 | The ERC provides support groups for individuals with eating disorders and their families. |
Helplines
| Resource Name | Contact Information | Description |
|---|---|---|
| National Eating Disorders Association (NEDA) | 1-800-931-2237 | NEDA provides confidential support and information to individuals and their families. |
| The Eating Disorders Coalition (EDC) | 1-888-375-7767 | The EDC provides confidential support and information to individuals and their families. |
| Eating Recovery Center (ERC) | 1-877-931-2237 | The ERC provides confidential support and information to individuals and their families. |
Online Resources
| Resource Name | Website | Description |
|---|---|---|
| National Eating Disorders Association (NEDA) | www.nationaleatingdisorders.org | NEDA provides information on eating disorders, treatment options, and support services. |
| The Eating Disorders Coalition (EDC) | www.eatingdisorderscoalition.org | The EDC provides information on eating disorders, treatment options, and support services. |
| Eating Recovery Center (ERC) | www.eatingrecoverycenter.com | The ERC provides information on eating disorders, treatment options, and support services. |
Call to Action
If you or someone you know is struggling with an eating disorder, it’s crucial to seek professional help. Eating disorders are serious mental illnesses that can have life-threatening consequences. However, with the right treatment, recovery is possible.Here are some resources that can help:
The National Eating Disorders Association (NEDA)
1-800-931-2237
The National Association of Anorexia Nervosa and Associated Disorders (ANAD)
1-847-831-3438
The Eating Disorders Coalition
https://www.eatingdisorderscoalition.org/
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/eating-disordersRemember, you are not alone in your struggles. Help is available, and recovery is possible.
Closure
Eating disorders are a complex and multifaceted issue, but recovery is possible. By raising awareness, providing support, and promoting early intervention, we can create a society where individuals with eating disorders feel empowered to seek help and live healthy, fulfilling lives.
FAQs
What are the most common types of eating disorders in Australia?
The most common types of eating disorders in Australia are anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder.
What are the warning signs of an eating disorder?
Warning signs of an eating disorder may include extreme dieting, excessive exercise, preoccupation with weight and body size, changes in eating habits, and emotional distress related to eating.
What are the risk factors for developing an eating disorder?
Risk factors for developing an eating disorder include genetics, personality traits, environmental factors, and exposure to media and social media that promote unrealistic body ideals.
What are the treatment options for eating disorders?
Treatment options for eating disorders may include psychotherapy, medication, nutritional counseling, and medical monitoring. The specific treatment plan will depend on the individual’s needs and the severity of the eating disorder.
Where can I find support for eating disorders in Australia?
There are many organizations and resources available to provide support for eating disorders in Australia, including the National Eating Disorders Collaboration (NEDC), the Butterfly Foundation, and Eating Disorders Victoria.